Building a Strong and Lasting Home Foundation: Key Components and Best Practices
Home » Structural » Foundation »
The Importance of a Quality Home Foundation
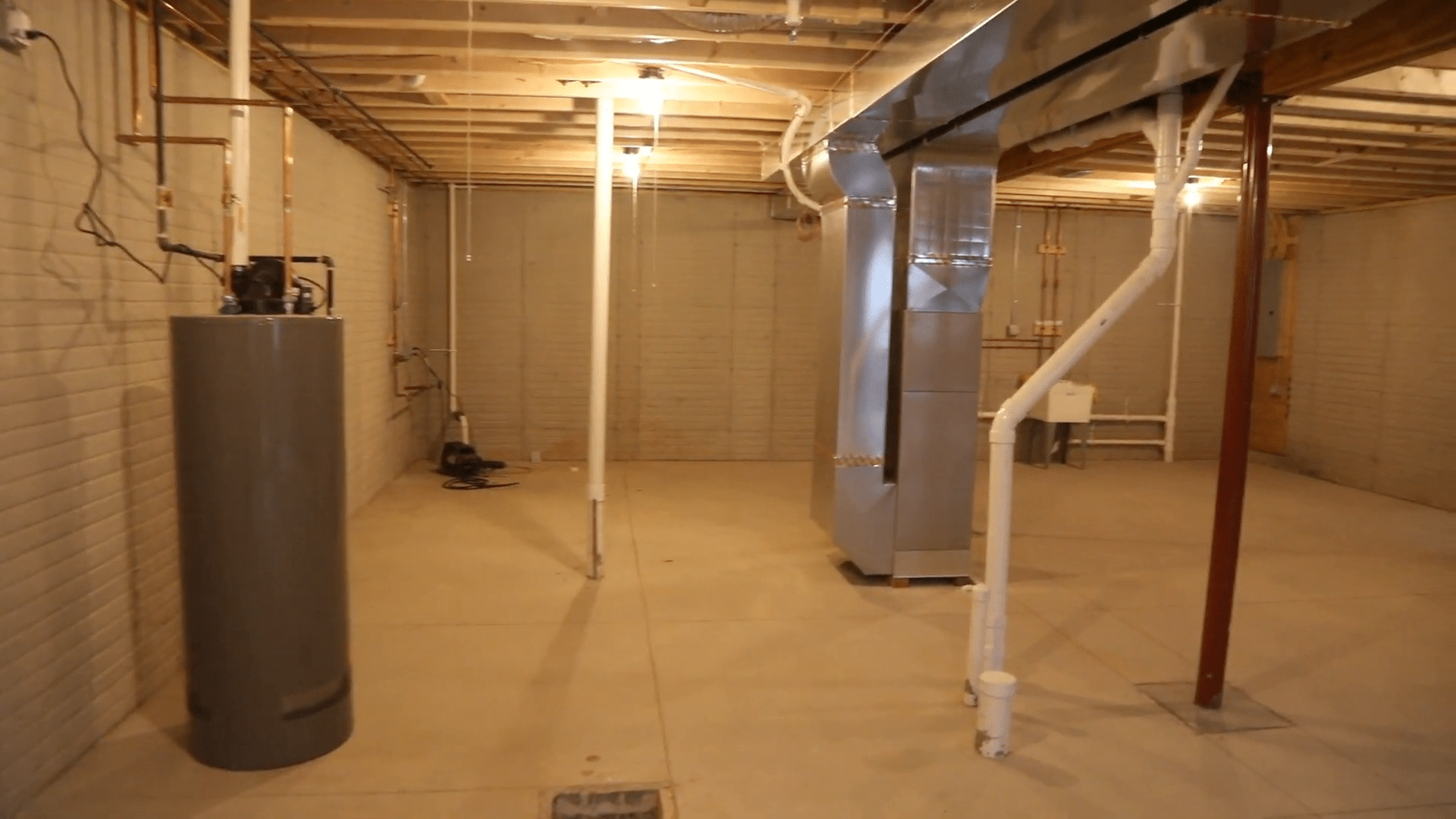
Ensuring the foundation of a new home is constructed correctly is vital for the structure’s longevity and stability. The foundation not only supports the entire building and its contents but also houses essential utilities like hot water heaters, furnaces, and laundry appliances. Even more, many homeowners opt to finish their basements, making it crucial that the foundation remains dry and structurally sound. A properly constructed foundation can last for generations, while a poorly built one can result in costly repairs and ongoing issues.
Three Critical Components
A home’s foundation comprises three critical components: the soil beneath the foundation, the waterproofing and drainage systems surrounding it, and the foundation structure itself. Each of these components plays a vital role in maintaining the integrity of the foundation. In this article, we will focus on the structural engineering of a poured concrete foundation for homes with basements. Understanding the best practices in foundation construction can help prevent structural issues and basement water leaks.
Anatomy of a Poured Concrete Foundation
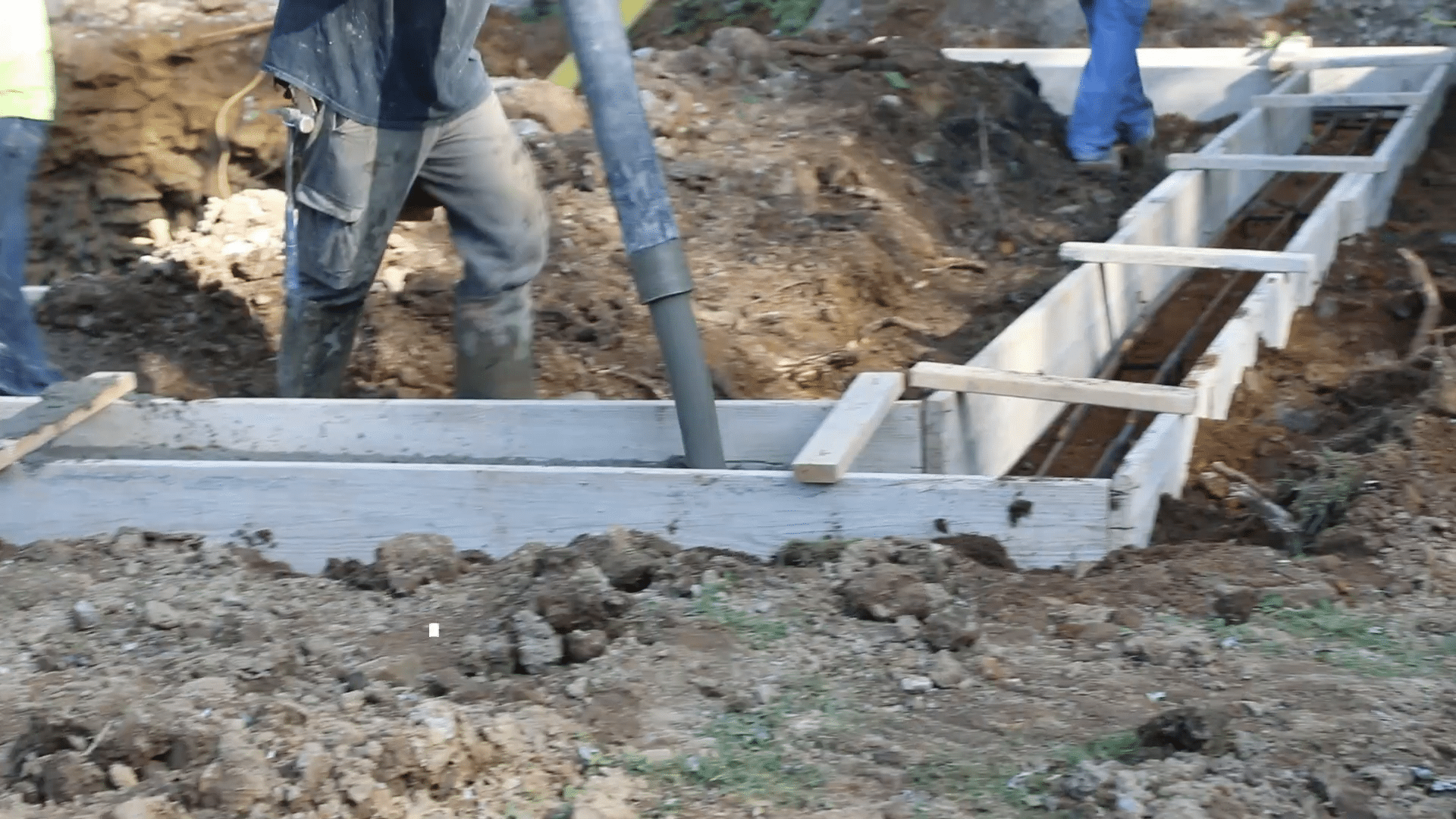
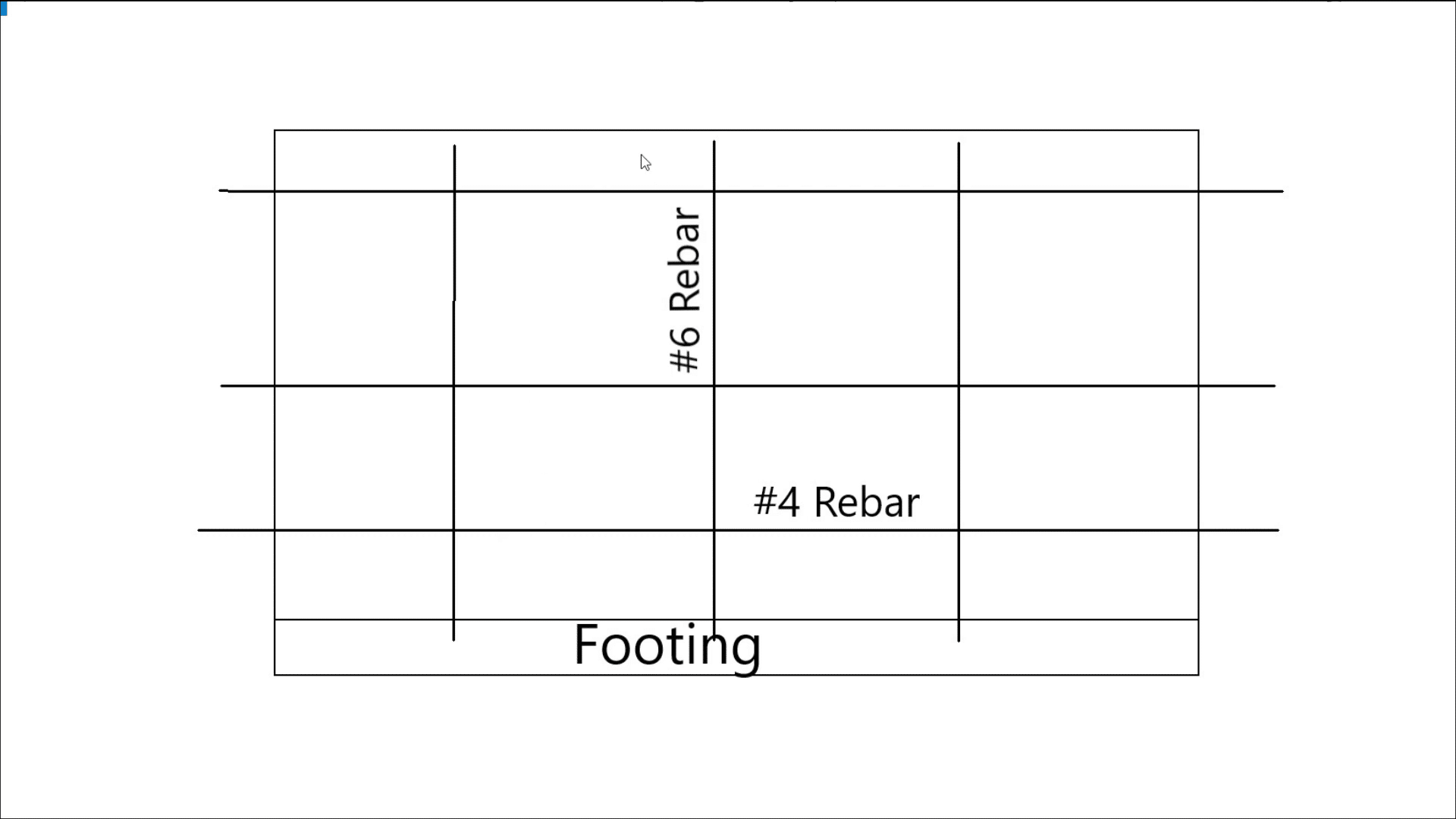
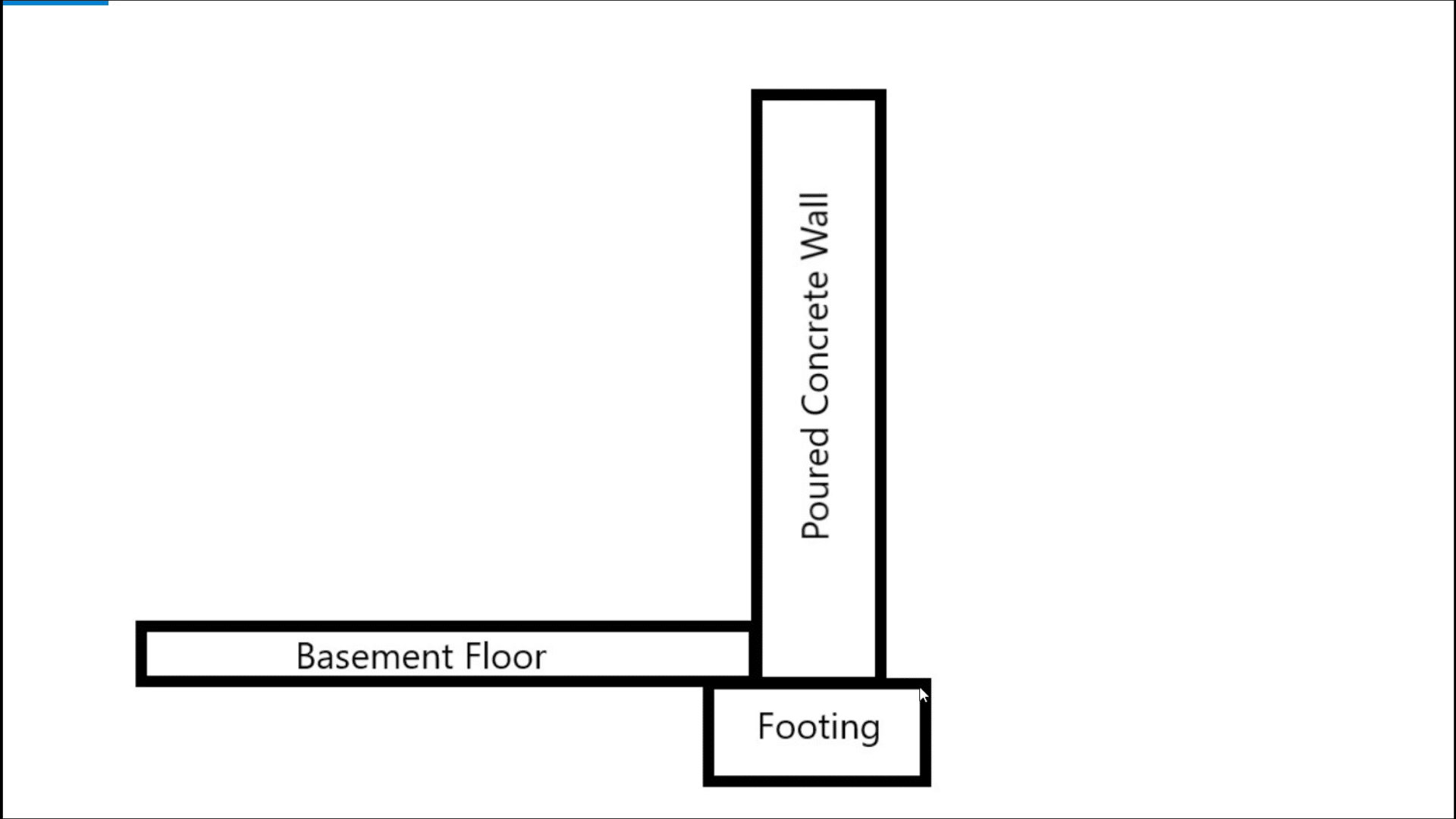
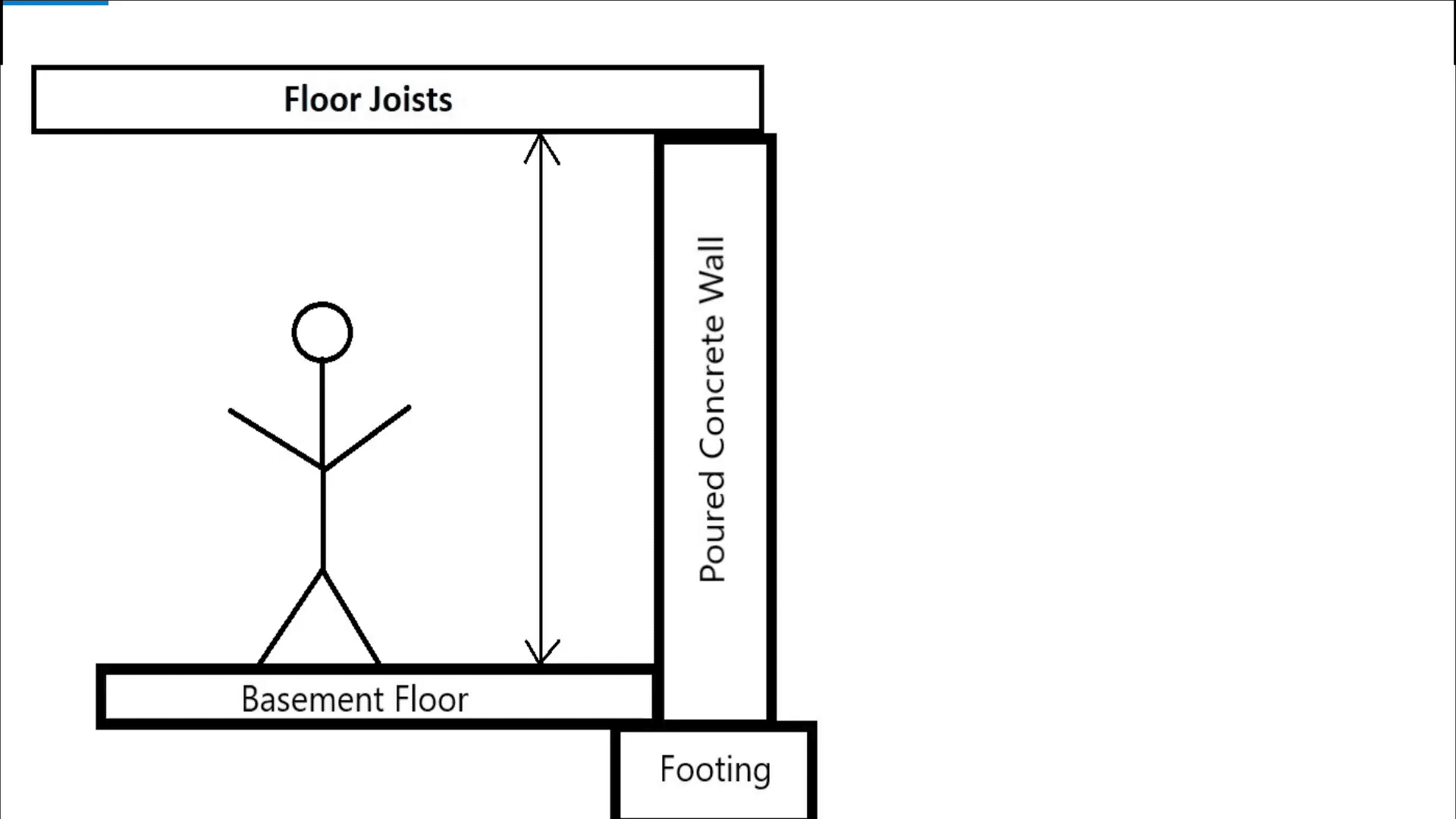
A typical poured concrete foundation consists of several key elements. The construction begins with the footing, a crucial part of the foundation that distributes the weight of the home across a larger area. For the project in question, the footing was 16 inches wide and 8 inches deep. The wall, which is poured on top of the footing, was nine feet tall and eight inches thick. This height allows for a finished basement with adequate headroom, making the basement feel like a traditional living space. The basement floor is poured later, resting on a ledge left by the footing, contributing to the overall stability of the foundation.
The Role of Rebar
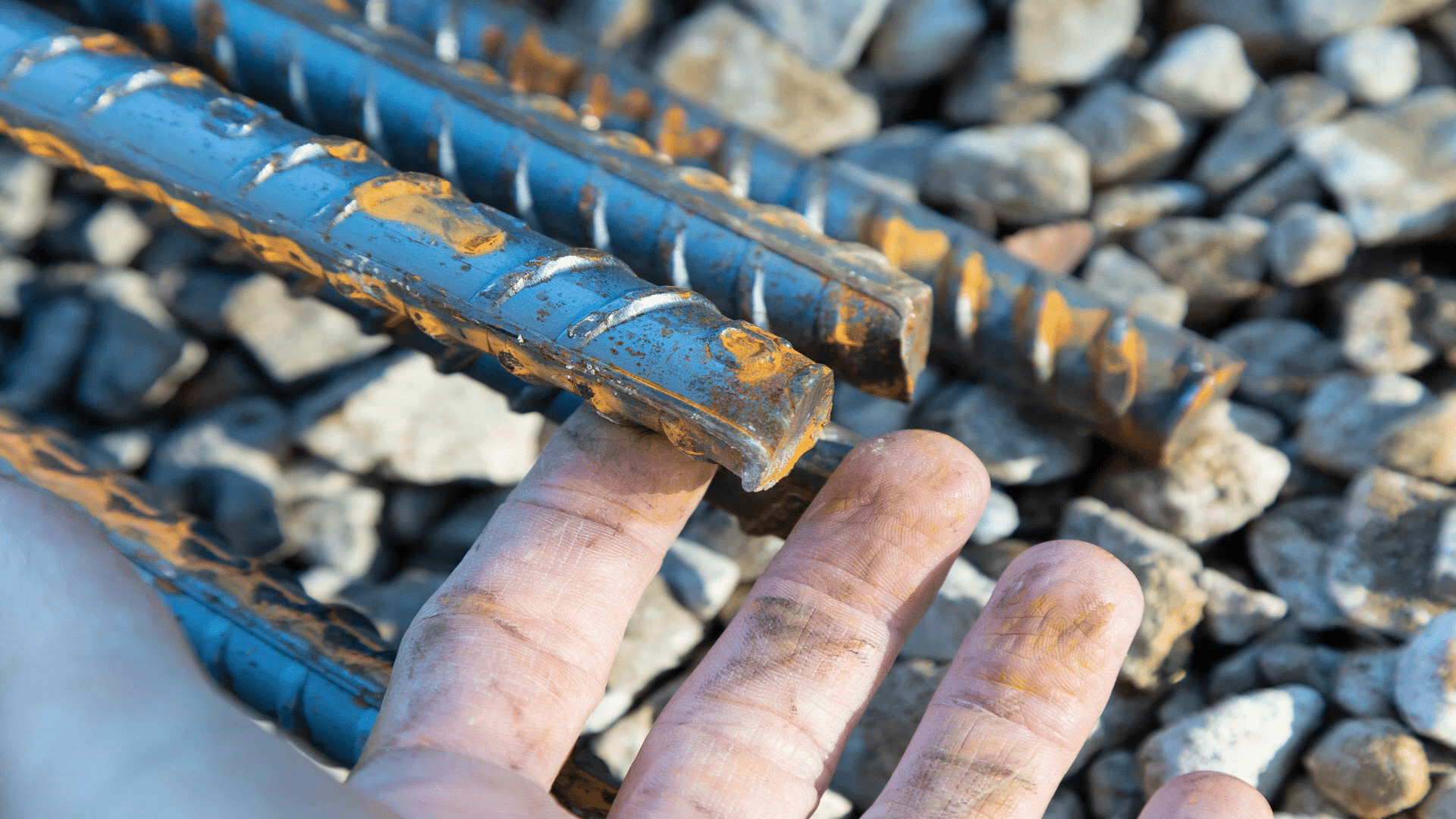
Reinforcing bars, or rebar, play a critical role in the strength and durability of a concrete foundation. In the footing, three strands of rebar were used along the bottom to provide support along its entire length. These bars are tied together at the ends to maintain structural integrity. The ridges on the rebar help the concrete grip onto it, ensuring the footing remains solid and prevents settlement that could lead to structural problems.
Importance of Level Footings
Ensuring the footing is level is crucial because the entire structure builds off this base. Uneven footings can lead to uneven walls and framing, which can compromise the structural integrity of the home. Concrete chairs are used to hold the rebar at the correct height within the footing, and nails mark the top level of the footing to ensure it is poured correctly.
Preventing Foundation Settlement
Settlement of the soil beneath the footing can lead to cracks and structural issues in the foundation. The rebar in the footing helps prevent these problems by providing additional support. Not every crack in a foundation wall indicates a structural problem, but displacement (vertical or horizontal movement) within a crack can be a sign of trouble. Displacement can also breach the waterproofing membrane, leading to water leaks in the basement.
Concrete Placement and Pressure
When placing concrete between the forms to create the foundation wall, it is essential to ensure a solid mass with no voids, as gaps can create weak spots. Once the forms are removed, and the excavation contractor backfills around the foundation, the soil exerts pressure on the walls. To counteract this pressure and prevent bowing, vertical and horizontal rebar is placed within the wall. Vertical rebar is spaced every three feet along the wall’s length, while horizontal rebar is placed in the lower, middle, and upper thirds of the wall.
Concrete Strength
Another best practice in foundation construction is to use concrete with a minimum design strength of 2500 pounds per square inch (psi) for the footings and 3000 psi for the walls. This specification ensures the concrete can withstand the loads and pressures it will encounter over its lifetime.
Additional Considerations
While the focus has been on the structural engineering of the foundation, it is also essential to consider the soil conditions and proper waterproofing and drainage systems. Soil stability and composition significantly impact the foundation’s performance. Conducting soil tests and using appropriate soil preparation techniques can prevent future settlement issues. Additionally, proper waterproofing and drainage systems around the foundation help prevent water infiltration, which can lead to structural damage and mold growth in the basement.
Conclusion
Constructing a quality foundation for a new home involves careful consideration of various factors, including the soil, waterproofing, drainage, and structural engineering. By following best practices such as using adequate rebar, ensuring level footings, and using high-strength concrete, homeowners can build a foundation that will stand the test of time and provide a solid base for their home. Taking these steps not only protects the investment in the property but also ensures the safety and comfort of its occupants for years to come.